Project
Agroecological assessment of the cup plant (Silphium perfoliatum L.)
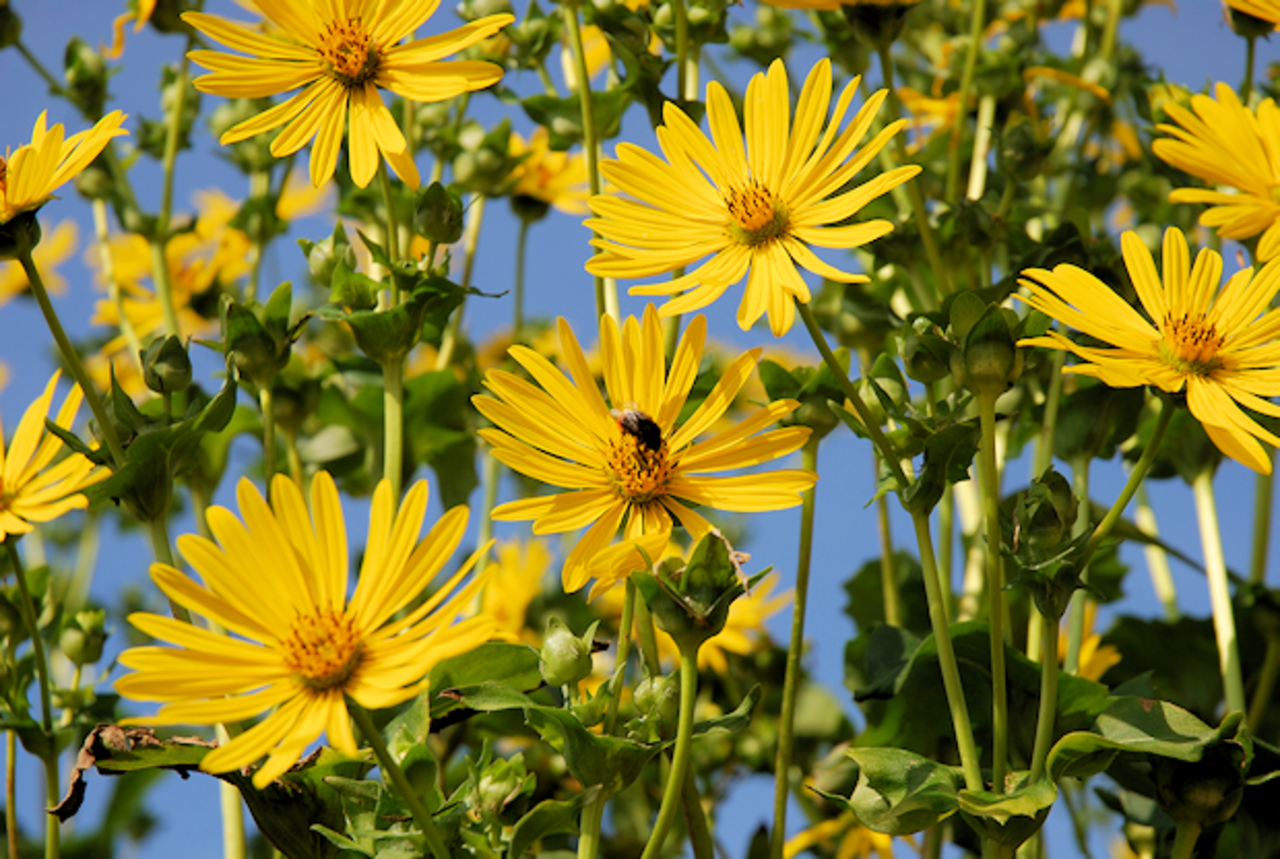

Agroecological assessment of the cup plant (Silphium perfoliatum L.) as a biomass crop of the future
The cup plant (Silphium perfoliatum L.) is a permanent energy crop which could complement maize as a feedstock for biogas. We investigate the importance of Silphium for biodiversity within the agroecosystem.
Background and Objective
To counteract short maize crop rotations and monotonous agricultural landscapes the cup plant Silphium perfoliatum with its high yielding ability is a promising candidate for biomass production. Its perennial lifecycle, long-lasting flowering period and low tillage imply positive effects on biodiversity and ecosystem services. Experience from agricultural practice also indicates a comparatively high drought tolerance of S. perfoliatum.
The project aims at quantifying the impact of Silphium on biodiversity and ecosystem services in agroecosystems. A further focus of the project is on the water balance of Silphium under different environmental conditions. The results of the project will help optimizing the cropping system of S. perfoliatum and understanding its interactions with other crops. Based on our results we will be able to ponder arguments for the commercial development of this novel energy crop from an agroecological perspective.
Target Group
Approach
Workpackage 1 on aboveground biodiversity has a focus on quantifying the food resources (nectar and pollen) provided by Silphium and identifying the community of flower visitors within the crop. A further focus is on interactions between Silphium and other crops in the landscapes and surrounding the fields. We conduct our research on 17 farms in Lower Saxony and on experimental plots in Thuringia.
Data and Methods
Our Research Questions
Results
Thünen-Contact

Involved Thünen-Partners
Involved external Thünen-Partners
- Julius Kühn-Institut - Bundesforschungsinstitut für Kulturpflanzen (JKI)
(Quedlinburg, Braunschweig, Groß Lüsewitz, Kleinmachnow, Deutschland) -
Thüringer Landesanstalt für Landwirtschaft
(Jena, Deutschland)
Funding Body
-
Fachagentur Nachwachsende Rohstoffe e.V. (FNR)
(national, öffentlich)
Duration
2.2012 - 7.2015
Publications
- 0
Müller AL, Biertümpfel A, Friedritz Lennart, Power EF, Wright GA, Dauber J (2020) Floral resources provided by the new energy crop, Silphium perfoliatum L. (Asteraceae). J Apicult Res 59(2):232-245, DOI:10.1080/00218839.2019.1668140
- 1
Müller AL, Berger C, Schittenhelm S, Stever-Schoo B, Dauber J (2020) Water availability affects nectar sugar production and insect visitation of the cup plant Silphium perfoliatum L. (Asteraceae). J Agron Crop Sci 206(5):529-537, DOI:10.1111/jac.12406
- 2
Schittenhelm S, Dauber J, Schrader S (2016) Bericht über die Fachtagung "Die Durchwachsene Silphie, eine Energiepflanze der Zukunft? Perspektiven von der Pflanze bis zur Landschaft". J Kulturpfl 68(12):349-350
- 3
Müller AL, Dauber J (2016) Hoverflies (Diptera: Syrphidae) benefit from a cultivation of the bioenergy crop Silphium perfoliatumL.(Asteraceae) depending on larval feeding type, landscape composition and crop management. Agric For Entomol 18(4):419-431, DOI:10.1111/afe.12175
- 4
Müller AL, Friedritz Lennart, Dauber J (2016) Pollensegen für Honigbienen? Was die Durchwachsene Silphie leisten kann. Allg Dt Imkerzeitg(6):12-13
- 5
Dauber J, Müller AL, Schittenhelm S, Schoo B, Schorpp Q, Schrader S, Schroetter S (2016) Schlussbericht zum Vorhaben : Thema: Agrarökologische Bewertung der Durchwachsenen Silphie (Silphium perfoliatum L.) als eine Biomassepflanze der Zukunft ; Teilvorhaben 1: Ober- und unterirdische Biodiversität in Beständen der Durchwachsenen Silphie ; Teilvorhaben 2: Wasserhaushalt und Ökophysiologie der Durchwachsenen Silphie ; Laufzeit: 01.02.2012 bis 31.07.2015. Berlin: Bundesministerium für Ernährung und Landwirtschaft (BMEL), 126 p
- 6
Dauber J, Miyake S (2016) To integrate or to segregate food crop and energy crop cultivation at the landscape scale? Perspectives on biodiversity conservation in agriculture in Europe. Energy Sustain Soc 6:25, DOI:10.1186/s13705-016-0089-5
- 7
Dauber J, Bolte A (2014) Bioenergy: Challenge or support for the conservation of biodiversity? GCB Bioenergy 6(6):180-182, DOI:10.1111/gcbb.12188
- 8
Müller AL, Biertümpfel A, Friedritz Lennart, Dauber J (2014) The energy plant Silphium perfoliatum L. (Asteraceae) as a late pollen resource for the honey bee Apis mellifera L.. Mitt Entomol Verein Stuttgart 49(1):42-43
- 9
Dauber J, Brown C, Fernando AL, Finnan J, Krasuska E, Poinitka J, Styles D, Thrän D, Groenigen KJ van, Weih M, Zah R (2012) Bioenergy from "surplus" land: environmental and socio-economic implications. BioRisk 7:5-50, DOI:10.3897/biorisk.7.3036

![[Translate to English:] [Translate to English:]](/media/_processed_/e/3/csm_Demetra2_c8a192c0f8.jpg)
![[Translate to English:] [Translate to English:]](/media/_processed_/e/2/csm_Demetra1_Panorama_8557ee3b13.jpg)