
Institut für
FI Fischereiökologie
DAIMON Toolbox Fact Sheet Table
1: Munitions detection and identification
1.1: Munition detection procedure with a hydroacoustic and magnetometry equipment
1.2: Identification and visual inspection of detected munitions-like objects
1.3: Munitions identification via Neutron Activation Analysis (NAA)
2: Hazardous substances
2.1:Chemical analysis of CWA-related compounds in sediment with LC-MS/MS
2.2: Chemical analysis of CWAs and degradation products in sediment with GC-MS/MS
2.3: Chemical analysis of conventional munitions in sediment with GC-MS/MS
2.4: Chemical analysis of CWA-related compounds in pore water with LC-MS/MS
2.5: Chemical analysis of CWA-related phenylarsenic chemicals in bile
2.6: Chemical analysis of CWA-related phenylarsenic chemicals in cut fillet
2.7: Chemical analysis of CWA-related phenylarsenic chemicals in fish liver
2.8: Chemical analysis of CWA-related phenylarsenic chemicals in fish gills
2.9: Chemical analysis of CWA-related phenylarsenic chemicals in mussel soft tissue
2.10: Extraction of explosives and metabolites from fish bile
2.11: Analysis of explosives and metabolites via HPLC-QQQ-MS
3: Biological effects
3.1: Sampling of wild fish
3.3: Homogenisation of fish liver and mussel digestive gland tissues
3.4: Homogenisation of fish muscle and mussel gill tissues
3.5: Fulton’s Condition Factor (CF) in Fish
3.6: Condition Index (CI)
3.7: Hepatosomatic Index (HSI) in Fish
3.8: Glycogen – accumulation of primary energy reserve in mussels
3.9: Hematology – blood glucose level
3.10: Lipid peroxidation
3.11: Superoxide dismutase activity
3.12: Catalase activity
3.13: Glutathione peroxidase activity
3.14: Glutathione reductase
3.15: Glutathione S-transferase activity
3.16: Externally visible fish diseases (EVFD)
3.17: Fish liver histopathology
3.18: Lysosome membrane stability
3.19: Lipofuscinosis – pathological accumulation of lysosomal lipofuscin
3.20: Lipidosis – pathological accumulation of neutral lipids
3.21: Hematology - erythrocytes, hemoglobin, hematocrit and leucocrit
3.22: Hematology - differential white blood cell count
3.24: Acetylcholinesterase inhibition
3.25: Macroscopic liver neoplasms (MLN)
3.26: Micronucleus Assay (MN)
3.27: Gene transcription
4: Other approaches
4.1: The mussel caging approach
4.2: The fish caging approach
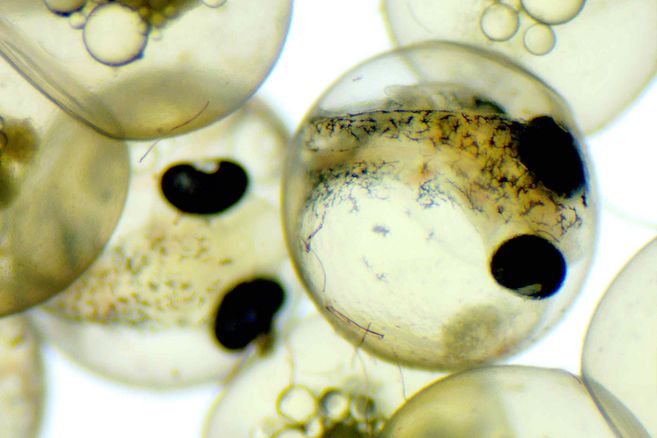
4.3: Zebrafish embryo acute toxicity test (FET)
4.4: Comet Assay (applied to zebrafish embryos)
4.5: Mussels lab exposure to warfare agents
4.6: Fluorescence assay for the detection of the activity of ABC transporters induced by toxicants




