Project
CarboHedge
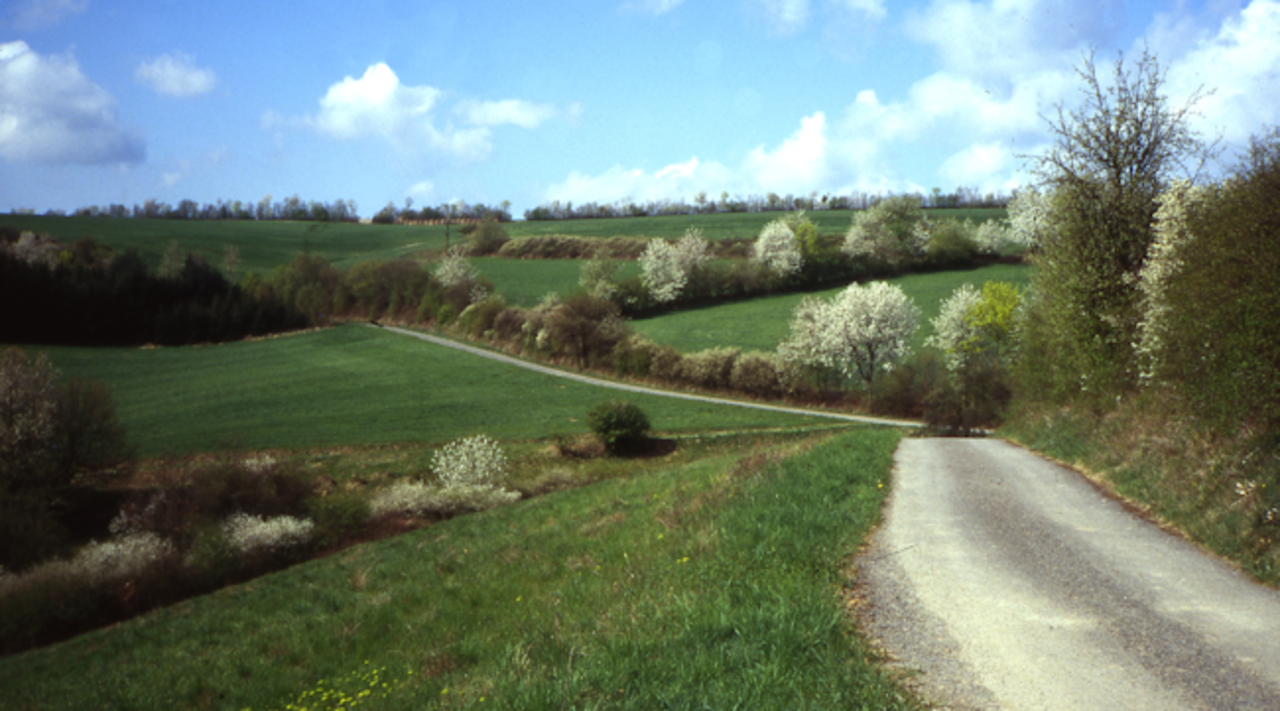

CarboHedge: Hedgerows and field copses in the emission inventories – Potential for carbon sequestration
Hedgerows for climate mitigation? - In the CarboHedge project we investigate how much organic carbon is stored in the soil and biomass of hedgerows and how hedgerows can contribute to climate mitigation by sequestering carbon in soil organic matter.
Background and Objective
Hedgerows and field copses are among the most important structures in agricultural landscapes and fulfil many functions. They have an important role for soil protection (e.g. erosion control) as well as for biodiversity and habitat connectivity. In addition, large amounts of organic carbon are stored in the above-ground biomass, the roots and the soils of hedgerows compared to adjacent agricultural areas. If new hedgerows are established, additional CO2 can be sequestered in the biomass and in the soil on the long term. Hedgerows therefore have great potential to contribute to climate mitigation. In the national greenhouse gas inventory, CO2 emissions and C-Sequestration resulting from the establishment or loss of hedgerows and field copses must be reported. However, the data currently reported is based on very few measurements and rough estimates.
Therefore in this project
- the carbon storage of hedgerows and field copses in Germany with a focus on soil organic carbon is quantified,
- the carbon sequestration potential for the establishment of new hedgerows in regions, where maximum synergies with the reduction of soil erosion, soil protection, biodiversity and climate protection can be achieved, is assessed and
- a concept for the reassessment of hedgerows and field copses in Germany’s greenhouse gas inventory will be developed.
Approach
Within the project, soils of hedgerows and adjacent agricultural areas are sampled representatively throughout Germany. Based on the collected data, the current carbon storage of hedgerows is determined and the potential for carbon sequestration is estimated depending on site conditions and hedgerow type. With the addition of further data sources, e.g. on soil erosion risk, target regions in Germany will be identified for the establishment of new hedgerows where maximum synergies can be achieved.
Results
DOI: 10.3220/PB1738753640000
Thünen-Contact

Involved Thünen-Partners
Duration
6.2019 - 5.2023
More Information
Project status:
finished
Publications
- 0
Drexler S, Don A (2025) CarboHedge - carbon sequestration via hedgerows. Braunschweig: Thünen Institute of Climate-Smart Agriculture, 2 p, Project Brief Thünen Inst 2025/07a, DOI:10.3220/PB1738753640000
- 1
Drexler S, Don A (2025) CarboHedge - CO2-Bindung durch Hecken. Braunschweig: Thünen-Institut für Agrarklimaschutz, 2 p, Project Brief Thünen Inst 2025/07, DOI:10.3220/PB1738753922000
- 2
Drexler S, Don A (2024) Carbon sequestration potential in hedgerow soils: Results from 23 sites in Germany. Geoderma 445:116878, DOI:10.1016/j.geoderma.2024.116878
- 3
Drexler S, Thiessen E, Don A (2024) Carbon storage in old hedgerows: The importance of below-ground biomass. GCB Bioenergy 16(1):e13112, DOI:10.1111/gcbb.13112
- 4
Drexler S, Gensior A, Don A (2021) Carbon sequestration in hedgerow biomass and soil in the temperate climate zone. Reg Environ Change 21:74, DOI:10.1007/s10113-021-01798-8
Project brief
 Project_Brief_2025_07a.pdf
320 KB
Project_Brief_2025_07a.pdf
320 KB

![[Translate to English:] [Translate to English:]](/media/_processed_/6/4/csm_titel_CO2Kampagne8_afeea2273e.png)
![[Translate to English:] [Translate to English:]](/media/_processed_/4/1/csm_titel_93px_CO2Kampagne8_9b0f3354d4.png)