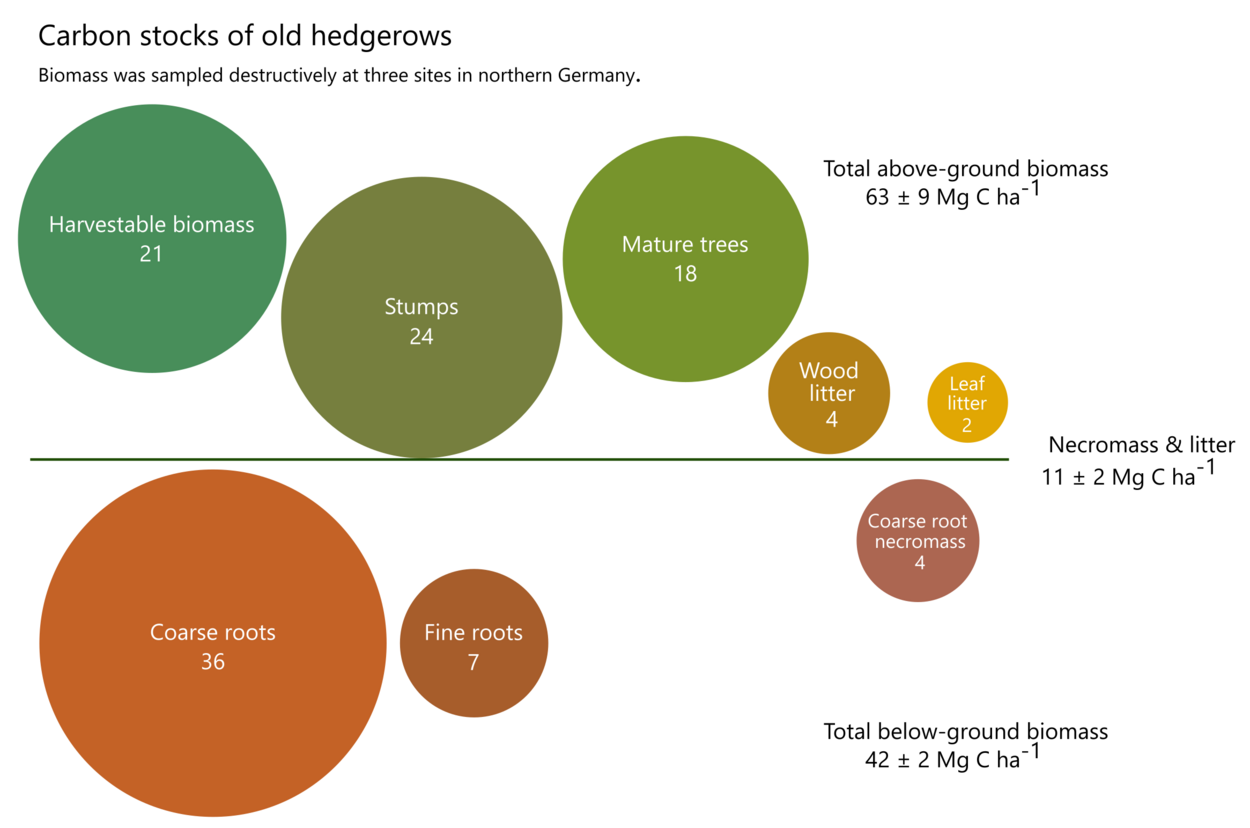
The establishment of hedgerows is increasingly discussed as a climate change mitigation measure, and positive and negative CO2 emissions caused by the establishment or removal of hedgerows must be reported in national greenhouse gas inventories. However, there have been few empirical studies on C storage in hedgerow biomass, and in particular data on belowground biomass in particular was missing. As part of the CarboHedge project, all biomass C pools were destructively sampled at old hedgerow sites in Schleswig-Holstein. Total long-term C storage in hedgerow biomass was 105 ± 11 Mg C ha-1, additionally 11 ± 2 Mg C ha-1 was stored in litter and necromass. Particularly important C pools in these hedgerow systems were the coarse roots >2mm (34% of the total biomass carbon stock), the stumps (22%) and the harvestable biomass (20%). The proportion of below-ground biomass in the total biomass was around 40%, and thus much higher than previously assumed. The study shows the great potential of hedgerows for C sequestration and can be used to better quantify the C storage of hedgerows.
Scroll to top

![[Translate to English:] [Translate to English:]](/media/_processed_/6/4/csm_titel_CO2Kampagne8_afeea2273e.png)
![[Translate to English:] [Translate to English:]](/media/_processed_/4/1/csm_titel_93px_CO2Kampagne8_9b0f3354d4.png)