Project
Optimized grass clover ley establishment

Optimized grass clover ley establishment through situation adjusted sowing techniques
Grass clover leys play a significant role in organic farming, both as animal feed and as an important crop rotation component that influences the productivity of subsequent arable crops. An optimized, situation-appropriate sowing technique aims to ensure that the potential of grass clover ley is fully utilized, both in livestock feeding and as a precursor crop in arable farming.
Background and Objective
Grass clover leys have a major role in organic farming, serving as both animal feed and a key component in crop rotation for the productivity of subsequent arable crops. This is partly due to its high nitrogen-fixing ability and its effect on reducing unwanted weeds through frequent cutting. A quick and complete establishment of grass clover leys that leads to high productivity in the first year of cutting use is crucial for efficient arable farming.
The "blank sowing" method after cereals is an established technique because good germination conditions are created by proper seedbed preparation. However, usually with this technique sowing is done relatively late in the year, so the plants start relatively small in the following spring. Alternatively, clover and grass can be undersown in cereals. In this case, the plants have time to establish themselves during the cereal growth period and can more efficiently utilize the growing season after the cereal harvest compared to those from blank sowing.
The objective of this project is to test different sowing techniques and timings for the establishment of grass clover leys after cereals, and to derive recommendations for optimized establishment techniques from the results.
Approach
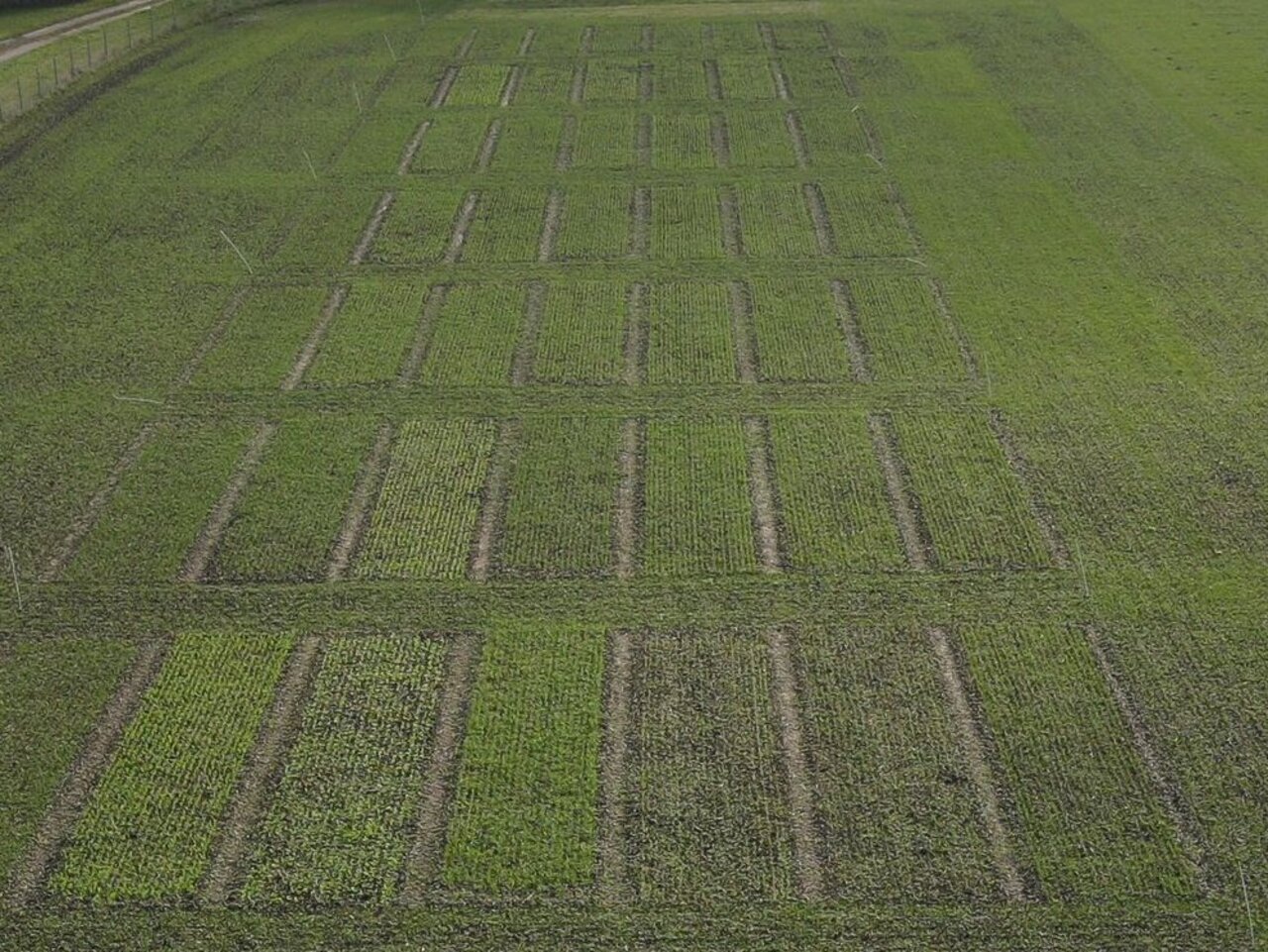
In a multi-year field trial, different sowing techniques and timings will be tested at the Trenthorst experiment station. In a randomized plot trial with four replications, the following methods will be tested:
- Undersowing in spring using drilling technique
- Undersowing in spring using drones
- Undersowing by drone in ripening cereals
- Direct sowing into stubble directly after harvest
- Blank sowing
In the same experiment different clover grass mixtures will be tested. Some of which contain drought tolerant grass, legumes and herbs. A detailed description can be found in the project DÜRAWEI – Drought-resistant pasture leys.
Our Research Questions
- How do the grass clover stands differ in development due to the different establishment methods?
- How does the productivity of the grass clover stands differ at various time points (Year 1, Year 2) and in cumulative production?
- Are there differences in nitrogen fixation between the establishment methods?
- What factors determine the success or failure of the individual methods?
Involved Thünen-Partners
Duration
9.2024 - 8.2029
More Information
Project status:
ongoing

![[Translate to English:] [Translate to English:]](/media/_processed_/8/e/csm_Bildschirmfoto_2021-03-03_bearb_fc48ac88bf.jpeg)
![[Translate to English:] [Translate to English:]](/media/_processed_/8/e/csm_Bildschirmfoto_2021-03-03_bearb_ba3ec0e9d7.jpeg)