ThEO
Land use in agricultural landscapes
Marcel Schwieder, Gideon Tetteh, Alexander Gocht, Stefan Erasmi
How is agricultural land used and how is its use changing? Satellites of the Copernicus program provide the basis for an area-wide and accurate inventory for the whole of Germany.
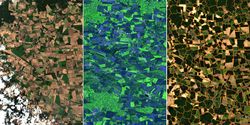
In contrast to other available data on land use (e.g. statistics, agricultural subsidy data), remote sensing data cover not only the UAA (UAA), but the entire open landscape (agricultural land, i.e. including uncultivated land).
Remote sensing thus provides the basis for an annual, timely, nationwide and small-scale survey of land use.
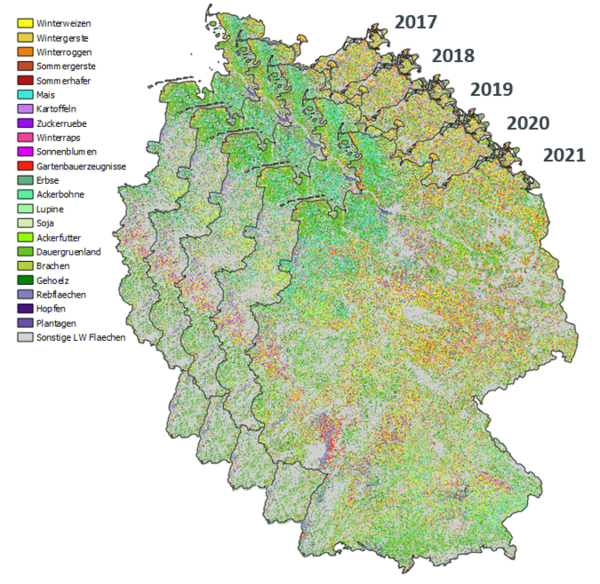
The Thünen Institute produces annual maps of land use in the open landscape for Germany on the basis of freely available satellite data from the Copernicus programme and other satellite data. The work is based on close cooperation with the Humboldt University of Berlin and the Leibniz Centre for Agricultural Landscape Research (ZALF).
The following products are currently available:
- Nationwide mapping of the main classes of agricultural land use (from 2017, annually).
- Nationwide mapping of grassland mowing for all grassland areas in the broad sense (permanent grassland, arable forage, fallow) (from 2017, annually).
The map products are each generated annually as a raster map (10 x 10 m resolution) and as a vector map (aggregation on automatically derived field boundaries) and can be viewed here. They are available for scientific use and the public on request. An overview of all available remote sensing products as well as the possibilities of data provision is given in the Thünen Earth Observation Atlas.
Agricultural statistics
The agricultural structure survey provides aggregated data on land use at intervals of three to four years, which are spatially and temporally disaggregated using estimators and samples. With the spatial data available, the statistical data can be validated and the procedures and results retrospectively optimised.
The EU agricultural policy
A core objective of the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) of the EU member states is to improve the condition and use of natural resources in the agricultural landscape. Satellite-based maps can help to understand the effectiveness of CAP measures, e.g. by showing changes in land use, crop diversity or landscape structure.








![[Translate to English:] Satellite-based Indicators for Monitoring Fen Re-wetting](/media/_processed_/1/5/csm_2724_Satellitenbasierte-Indikatoren_C-Hellmann_DJI_0076_ba59ce9f94.jpg)