In addition to the production of food and agricultural raw materials, agriculture is essential in providing environmental public goods for the benefit of rural areas and society.
The intensive forms of farming that are common in agriculture are often held responsible for the decline in biodiversity and species diversity in agricultural landscapes. The contribution of agriculture to global greenhouse gas emissions and the nutrient pollution it causes also require changes in the management of agricultural land and farm management.
Diverse agricultural landscapes are of great economic relevance for agricultural operations, but are also species-rich habitats and of increasing importance for society. Through the use of agricultural and environmental measures, agricultural landscapes can also represent valuable habitats. Agriculture is both contributing to, and affected by climate change. Many production methods that prevail in Germany are comparatively climate-efficient, but additional reduction measures are necessary to meet national climate targets.
In order to achieve these (sometimes competing) goals, the efficiency of the use of resources and agricultural land has to be improved. This, in turn, places the focus on the question how to foster sustainable land use. How can we achieve this important goal of sustainability in agriculture without losing the competitiveness on the markets? How can the protection of the environment play a greater role in operational decisions of farmers and value chain actors? And how can agricultural and environmental policies contribute to this?
As part of our research, we examine the questions of policy design and analyze consequences of agri- environmental policy instruments for individual farms and for the profitability of particularly environmental friendly and sustainable farming systems. By using economic modeling we examine the effects on agriculture and the environment in Germany, at European and global level. In order to identify relationships between landscape elements and agricultural management practices, we are working in collaboration with other research institutes and stakeholder groups. In addition, we address the question of how the effects of agri-environmental policy instruments in the agricultural sector could be better evaluated and how their cost-effectiveness could be increased from an agri-environmental policy perspective. We evaluate climate protection and adaption measures with regard to their reduction potential and their economic costs at farm level. In order to strengthen sustainability in agriculture, we are investigating how sustainable, resource-saving production can be determined and which processes and measures can be used.
Organic farming is considered to be particularly sustainable and is a separate area of work at the Thünen Institute.
Organic farming at the Institute of Farm Economics





![[Translate to English:] Brightspace](/media/_processed_/a/5/csm_interaction_Brightspace2_a186192d43.jpg)
![[Translate to English:] CatchHedge - Carbon sequestration of hedgerows and field copses](/media/_processed_/a/f/csm_CatchHedge_DSC_0275_3060ddf19f.jpg)







![[Translate to English:] Greenhouse gas mitigation on dairy farms - where to start - and how expensive will it be?](/media/_processed_/6/f/csm_2594_Fleckvieh_TI_Martin-Koechy_IMG_6471b_original_d3941fe0f8.jpg)
![[Translate to English:] HotSpots Erosion](/media/_processed_/d/3/csm_2510_20190524_Lamspringe_Erosion_Trompeterbusch_low_res_w_68439fae45.jpg)

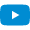
![[Translate to English:] InnoRind](/media/_processed_/7/c/csm_2532_Rind_ab_mitLogo_d3b7051c37.jpg)
![[Translate to English:] LAMASUS - Modellierung von Landnutzung und -management für eine nachhaltige Steuerung](/media/_processed_/9/a/csm_2579_Lamasus-color-positive_11dc120efd.png)






![[Translate to English:] The development of a harmonised set of minimum criteria for the assessment of sustainable action by agricultural enterprises in key business sectors.Focus on farms with milk production, arable farming and pig farming](/media/_processed_/c/6/csm_2694_MiniKriSet_AdobeStock_95004168_large_df2aa2e6f4.jpg)













![[Translate to English:] The three NUTRI2CYCLE pillars and the 8 key agro-typologies under investigation Nutri2Cycle - Nurturing the Circular Economy](/media/_processed_/a/1/csm_2010_Bild_webpage_496983add9.jpg)