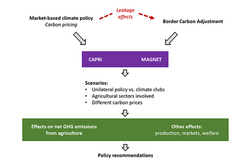
The EU's common agricultural policy affects the situation and development of agriculture by numerous supportive and regulatory measures. Given the extraordinarily dynamic change of the environment and social requirements facing agriculture, the EU's agricultural policy is under constant review. Against this background, we develop a scientific basis for effective policy-making. Firstly, we evaluate current instruments of EU agricultural policy, such as the farm investment support. Secondly, we analyze options for future policy development, e.g. the future of direct payments or the consequences of the abolition of the milk quota system. Together with the Institute for Rural Studies and the Institute of Market Analysis, we also investigate the impact of different options for a fundamental reform of the CAP after 2020, and thus support policy makers to develop a targeted and efficient overall concept.
In the Institute of Farm Economics, we focus on the question of how political decisions affect farms and how they can adapt to the related changes in framework conditions. Focus of our research is the Germany-wide assessment of the impact of changing conditions on production, land use, income and environment in differently structured farms. In addition, we provide answers to the question of how the economic performance of farms evolves and which individual adaptation strategies exist. To this end we use a variety of different data sources and methods, e.g. the German Farm Accountancy Data Network [Link] and, within the Thünen Model Network the farm models FARMIS as well as TIPICAL and TYPI-CROP of the agri benchmark network.



![[Translate to English:] 5-State-Evaluation: Effects of farm income diversification support](/media/_processed_/4/0/csm_2552_Hofladen_BernhardForstner_feb585bcfc.jpg)



![[Translate to English:] Brightspace](/media/_processed_/a/5/csm_interaction_Brightspace2_a186192d43.jpg)
![[Translate to English:] CatchHedge - Carbon sequestration of hedgerows and field copses](/media/_processed_/a/f/csm_CatchHedge_DSC_0275_3060ddf19f.jpg)






![[Translate to English:] Impact assessment with the CAPRI model of a plant-based dietary change](/media/_processed_/9/3/csm_F_Collage_2589_TRIP_72eab25133.jpg)
![[Translate to English:] LAMASUS - Modellierung von Landnutzung und -management für eine nachhaltige Steuerung](/media/_processed_/9/a/csm_2579_Lamasus-color-positive_11dc120efd.png)