Dossier
Horticulture
Walter Dirksmeyer, Hildegard Garming | 29.10.2025
Horticulture is characterized by a very large variety of products and production systems. Hundreds of different plant species are cultivated in the sectors of vegetables, fruit, ornamental plants, nurseries and perennials. Compared to arable farming, a very high added value is achieved in relation to the area.
Horticultural production systems include
- open field and protected cultivation,
- perennial permanent crops and short crops of a few weeks,
- cultivation in soil, substrate or nutrient solutions.
The production of fruits, vegetables and other horticultural products is a very intensive form of land management with high added value compared to arable farming. Horticulture covers only 1.3 % of the agricultural land in Germany, but generates about 12% of the gross value added and employs almost 15% of the labor force in agriculture.
This high intensity of use of labor and capital, as well as nutrients, crop protection, substrates and energy - for example in greenhouse production – also means that changes in the political, legal or market conditions can have a major impact on the profitability and competitiveness of horticultural production. Major questions for our working group are how economic performance of farms is affected e. g. by rising energy costs or changes in the legal framework for fertilizer use and how horticultural farms adapt strategically to such challenges. The sustainability of horticultural production also plays an important role. What costs and benefits arise for farms from climate protection through a reduction in the use of peat for planting substrates or humus build-up, and what are ecologically effective and economically efficient measures?
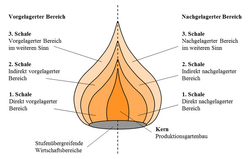
The key challenge for horticultural value chains is to maintain freshness and quality for rapidly perishable products such as fruits and vegetables but also flowers or ornamental plants. Analyses of the economic efficiency and competitiveness of horticultural production systems, e. g. with regard to food losses or digitalization, must therefore always take the entire value chain into account.
German horticulture faces intense international competition: around 60% of the vegetables and more than 85% of the fruit consumed in Germany are imported from other countries. We are working on international aspects of horticulture, such as comparing the production systems and costs of selected crops in different countries or climatic zones, as part of the agri benchmark Horticulture network.
Download Service
The horticulture fact sheets (Steckbriefe zum Gartenbau) provide a brief, annually updated overview of the supply situation and production structures for horticultural products in Germany.
The depth of observation differs between the individual horticultural production sectors due to the varying availability of data.
The fact sheets are published in German only.






![[Translate to English:] Structural change and competitiveness of the German horticultural sector](/media/_processed_/d/d/csm_1469_Gemuese_2021_600-dpi_groesser_3000_4bdfd29c63.png)






![[Translate to English:] HortiCo 4.0](/media/_processed_/7/4/csm_HortiCo40_Logo_MitClaim_RGB_9f895ba1a5.png)